- Your cart is empty Browse Shop

Fertilizers
CALCIUM NITRATE
Chemical Formula: Ca(NO₃)₂
HS Code: 31059000
NPK Grade : 15.5-0-0 + 18.5% Ca
What is Calcium Nitrate?
Calcium Nitrate is a highly water-soluble, nitrogen-rich fertilizer that also supplies plant-available calcium. It is a dual-nutrient product commonly used in agriculture to support strong plant growth and structural cell development. It is also applied in various industrial sectors.
It appears as white granules or flakes, odorless and non-volatile, and is highly hygroscopic (absorbs moisture quickly from the air).
Types of Calcium Nitrate
1. Agricultural Grade (Granular/Crystalline)
- Contains nitrate nitrogen and soluble calcium
- Ideal for fertigation, greenhouse farming, open-field crops
- Commonly used for fruiting and vegetable crops
2. Liquid Grade (Calcium Ammonium Nitrate Solution)
- Used in controlled fertigation systems, hydroponics, and precision agriculture
Uses of Calcium Nitrate
Agricultural Uses
- Supplies fast-acting nitrate nitrogen (NO₃⁻) and calcium (Ca²⁺)
- Prevents and corrects calcium deficiency (e.g. blossom end rot in tomatoes, tip burn in lettuce)
- Improves fruit firmness, shelf life, and stress resistance
- Ideal for:
- Tomatoes, peppers, cucumbers, lettuce, apples, grapes
- Hydroponic systems and soilless media
Industrial Uses
- Concrete additive to improve setting time and durability
- Anti-freezing agent in construction during cold weather
- Used in latex coagulation, cooling brines, and fertilizer blends
Typical Specifications – Agricultural Grade Calcium Nitrate
| Parameter | Typical Value |
|---|---|
| Total Nitrogen (as N) | Min. 15.5% |
| Nitrate Nitrogen (NO₃⁻) | Min. 14.4% |
| Ammoniacal Nitrogen | Max. 1.1% |
| Water-Soluble Calcium (Ca) | Min. 18.5% |
| Moisture | Max. 0.5% |
| Appearance | White granular or crystalline |
| Solubility in Water | 100% |
| pH (1% solution) | 5.0 – 7.0 |
| Chloride Content | < 0.2% |
Packing Options
- 25 kg and 50 kg woven bags with inner PE liner
- 1 MT jumbo bags for bulk shipments
All products come with:
- SGS/BV Inspection (on demand)
- Certificate of Analysis (COA)
- Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS)
- REACH & ISO documentation (where applicable)
Fertilizers
DI-AMMONIUM PHOSPHATE (DAP)
Chemical Formula: (NH₄)₂HPO₄
HS Code: 31053000
What is DAP?
Di-Ammonium Phosphate (DAP) is the most widely used phosphatic fertilizer in the world. It contains high concentrations of both nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) – essential nutrients for plant growth. It is known for its excellent nutrient balance and high nutrient availability.
DAP appears as granular, free-flowing, non-dusty particles, usually light brown, gray, or off-white in color, depending on the production process.

Types of DAP
While the chemical composition of DAP remains generally standard, the product is available in different grades based on:
- 1.Color & Appearance:
- Brown/Gray DAP (most common)
- White/Off-white DAP (premium, less impurities)
- 2.Granule Size:
- Standard DAP: Smaller granules (2–4 mm)
- Granulated DAP: Larger, uniform particles for mechanical application
- 3.Purity & Application:
- Agricultural Grade: Used for direct soil application
- Industrial Grade: Used in fire retardants, metal finishing, and detergents
Uses of DAP
Agricultural Uses
- Primary source of phosphorus and nitrogen in crop cultivation
- Improves root development, flowering, and early crop growth
- Used for a wide range of crops: wheat, rice, cotton, corn, vegetables, etc.
- Suitable for:
- Base application (basal dose)
- Fertigation
- Blending with other fertilizers
Industrial Uses
- Used in fire extinguishers (dry chemical extinguishing agents)
- Component in fire retardant coatings and paints
- Ingredient in detergents, metal cleaners, and fermentation processes
Typical Specifications (Agricultural Grade DAP 18-46-0)
| Parameter | Typical Value |
|---|---|
| Total Nitrogen (as N) | Min. 18.0% |
| Available Phosphate (P₂O₅) | Min. 46.0% |
| Moisture Content | Max. 1.5% |
| Granule Size | 90% between 2–4 mm |
| Biuret | Max. 1.5% |
| Free from lumps | Yes |
| Appearance | Granular, free-flowing |
Industrial DAP may have higher purity or be in powder/crystal form depending on its end-use.
Packing Options
- 50 kg PP woven bags with inner liner
- 25 kg bags (for specialty/retail markets)
- 500 kg & 1000 kg Jumbo Bags – bulk shipments
- Bulk in Containers – for large agricultural or industrial buyers
Export Markets Served
OPS ASIA LIMITED supplies DAP to:
- India, Vietnam, China, Turkey, South Korea
- GCC countries – UAE, Oman, Qatar
- USA, Brazil, Mexico
- Europe – Eastern & Western regions
All shipments are arranged with SGS/BV certification, ensuring compliance with international quality standards.

Fertilizers
MONO-AMMONIUM PHOSPHATE (MAP)
Chemical Formula: NH₄H₂PO₄
HS Code: 31051000
NPK Grade : 12-61-0
HS Code: 31051000
NPK Grade : 12-61-0
What is MAP?
Mono-Ammonium Phosphate (MAP) is a highly concentrated phosphatic fertilizer containing 12% nitrogen (N) and 61% phosphorus pentoxide (P₂O₅). It is one of the most efficient sources of phosphorus and is widely used in both agriculture and industrial processes.
MAP is water-soluble, non-hygroscopic, and typically appears as white, off-white, or grayish free-flowing granules or crystals.
Types of Calcium Nitrate
1. Agricultural Grade MAP (Granular or Crystalline)
- Used in open-field farming
- Applied directly to soil or through fertigation
- Ideal for high-phosphorus crop stages
2. Water-Soluble MAP (Crystal/Powder Form)
- Ultra-pure grade for greenhouse farming, drip irrigation, and hydroponics
- Used in fertigation systems or foliar sprays
3. Industrial Grade MAP
- Used in flame retardants, fermentation, metal treatment, and cleaning compounds
Uses of MAP
Agricultural Uses
- Provides readily available phosphorus and nitrogen to plants
- Enhances root development and early plant growth
- Used in fertigation, broadcasting, and soil application
- Ideal for:
- Vegetables, fruits, cereals, and oilseed crops
- High-efficiency starter fertilizer
Industrial Uses
- Used in fire-retardant coatings and chemicals
- Component in cleaning agents, metal treatment solutions
- Applied in fermentation processes and yeast cultivation
Typical Specifications (Agricultural Grade MAP 12-61-0)
| Parameter | Typical Value |
|---|---|
| Total Nitrogen (as N) | Min. 12.0% |
| Available P₂O₅ | Min. 61.0% |
| Moisture Content | Max. 0.5% |
| Water Solubility | 100% Soluble |
| pH of 1% solution | 4.5 – 4.8 |
| Appearance | White/Off-white crystals or granules |
| Chloride Content | Negligible (Cl– free) |
For water-soluble MAP, particle size is finer (powder or crystalline), and purity is higher.
Packing Options
- 25 kg and 50 kg PP woven bags with PE liner
- 1 MT jumbo bags for bulk agricultural users
All shipments comply with international standards and include SGS/BV certifications on request.
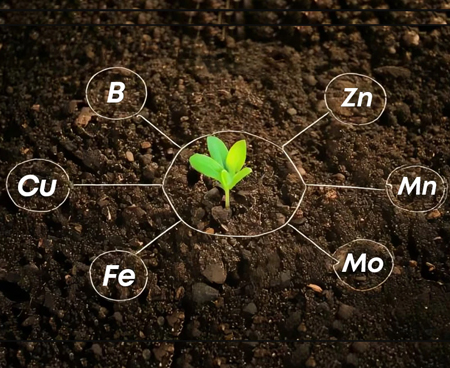
Fertilizers
MICRONUTRIENTS
Category: Essential Plant Nutrients (Secondary & Trace Elements)
HS Code: Varies by compound (e.g. Zinc Sulfate: 28332990)
What are Micronutrients?
Micronutrients are essential nutrients required by plants in small (micro) quantities but are vital for plant metabolism, enzyme function, photosynthesis, and overall growth. A deficiency in even one micronutrient can drastically reduce crop yield and quality.
Micronutrients complement macronutrients (NPK) and are especially critical in modern high-yield farming systems.
Types of Micronutrients
Micronutrients are supplied as either inorganic salts or chelated forms for better absorption.
| Element | Typical Form (Inorganic) | Chelated Form | Role in Plants |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zinc (Zn) | Zinc Sulphate (ZnSO₄) | Zn-EDTA, Zn-DTPA | Growth hormones, enzyme activation |
| Iron (Fe) | Ferrous Sulphate (FeSO₄) | Fe-EDTA, Fe-DTPA | Chlorophyll formation (green color) |
| Manganese (Mn) | Manganese Sulphate (MnSO₄) | Mn-EDTA | Photosynthesis, respiration |
| Copper (Cu) | Copper Sulphate (CuSO₄) | Cu-EDTA | Enzyme activity, disease resistance |
| Boron (B) | Borax, Boric Acid | – | Reproduction, pollen tube growth |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | Sodium Molybdate, Ammonium Molybdate | – | Nitrogen fixation |
| Magnesium (Mg) | Magnesium Sulfate (Epsom salt) | – | Chlorophyll production, enzyme cofactor |
| Calcium (Ca) | Calcium Nitrate, Calcium Chloride | – | Cell wall strength, fruit firmness |
Uses of Micronutrients
- Correct deficiencies of specific trace elements in soil
- Improve plant metabolism, fruit set, and disease resistance
- Used in:
- Soil application
- Foliar spray
- Fertigation systems
- Suitable for vegetables, fruits, cereals, cash crops, and floriculture
Typical Specifications (Example – Zinc Sulphate Monohydrate)
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Zinc (Zn) | Min. 33% |
| Purity | Min. 98% |
| Insoluble matter | Max. 0.05% |
| pH (5% solution) | 4.0 – 5.5 |
| Appearance | White powder or crystals |
| Solubility | Fully water-soluble |
Chelated micronutrients have slightly different specifications (e.g. Zn-EDTA: Zn ≥12%)
Packing Options
- 25 kg HDPE bags with inner liner (for bulk users)
- 1 kg, 5 kg, 10 kg laminated pouches (for retail/foliar grade)
All shipments come with:
- MSDS & COA
- Third-party test reports (SGS/BV)
- Organic/Non-GMO/REACH-compliant certifications (where applicable)

Fertilizers
Rock Phosphate
OPS ASIA LIMITED, based in Hong Kong, is a globally recognized trading and export company specializing in the supply of rock phosphate in various grades and packaging options. We source from top producers and supply to clients across the fertilizer, agriculture, and chemical manufacturing industries.
With a strong logistics network and commitment to product consistency, we help our partners access high-purity rock phosphate at competitive prices — delivered reliably across Asia, Africa, the Middle East, and Europe.
Our Rock Phosphate Product Range
We offer rock phosphate with varying P₂O₅ (phosphorus pentoxide) content to match the specific needs of your application:
High-Grade Rock Phosphate
- P₂O₅ content: 30%–34%
- Ideal for phosphatic fertilizer manufacturing
Medium-Grade Rock Phosphate
- P₂O₅ content: 24%–29%
- Used in direct application to soil and blended fertilizers
Low-Grade Rock Phosphate
- P₂O₅ content: Below 24%
- Suitable for soil enrichment in acidic conditions
Packaging Options
We provide rock phosphate in customized packing formats for bulk and retail needs:
| Packing Type | Size Options | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Jumbo Bags (FIBC) | 1 MT / 1.25 MT | Industrial & agricultural bulk |
| PP Woven Bags | 25 kg / 50 kg | Retail & distribution channels |
| Bulk Shipments | In containers or vessels | High-volume fertilizer production |
| Palletized Shipments | Optional shrink-wrapping | Export-ready secured loading |
All packaging complies with international shipping and safety regulations.
Applications of Rock Phosphate
Rock phosphate is an essential raw material in agriculture and industry:
- Fertilizer Industry: Key source for manufacturing SSP (Single Super Phosphate) and DAP (Di-Ammonium Phosphate)
- Direct Soil Application: Used in organic and regenerative farming for slow-release phosphorus
- Chemical Industry: Base material for producing phosphoric acid, animal feed supplements, and detergents
- Industrial Use: Catalyst in metal treatment and glass manufacturing
Why Choose OPS ASIA LIMITED?
- Global Export Capability
- Wide Grade Selection (Low, Medium, High P₂O₅)
- Flexible Packing Options
- Sourced from Trusted Mines
- End-to-End Documentation & Logistics
- Reliable Supply for Fertilizer Producers and Traders
We ensure a stable supply chain, even in fluctuating markets, and offer long-term contracts for consistent rock phosphate delivery.
Markets We Serve
OPS ASIA LIMITED exports rock phosphate to:
- India
- Bangladesh & Southeast Asia
- Middle East (UAE, Saudi Arabia, Oman)
- East & West Africa (Kenya, Nigeria, Ethiopia)
- Europe & CIS countries

Fertilizers
MONO POTASSIUM PHOSPHATE (MKP)
Chemical Formula: KH₂PO₄
HS Code: 31056000
NPK Grade: 0-52-34
What is MKP?
Mono Potassium Phosphate (MKP) is a high-purity, fully water-soluble phosphate fertilizer that provides 52% phosphorus (P₂O₅) and 34% potassium (K₂O). It is chloride-free, sodium-free, and ideal for use in fertigation, foliar spraying, and high-efficiency agriculture. MKP also serves as a buffering agent and ingredient in industrial applications.
MKP appears as a white crystalline powder and is valued for its quick absorption and non-reactivity with other fertilizers.
Uses of MKP
Agricultural Uses
- Provides high phosphorus and potassium with zero nitrogen
- Supports root development, flowering, and fruit setting
- Improves plant resistance to disease and environmental stress
- Widely used in:
- Vegetables
- Fruits (grapes, citrus, mango)
- Flowers and ornamental crops
- Hydroponic systems
Typical Specifications – Agricultural Grade MKP
| Parameter | Typical Value |
|---|---|
| Phosphorus (P₂O₅) | Min. 52.0% |
| Potassium (K₂O) | Min. 34.0% |
| Moisture | Max. 0.5% |
| pH (1% solution) | 4.2 – 4.6 |
| Water Solubility | 100% |
| Appearance | White crystalline powder |
| Chloride Content | < 0.2% |
| Heavy Metals (as Pb) | < 10 ppm |
Packing Options
- 25 kg HDPE laminated bags with inner liner
- 50 kg woven bags (on request)
All shipments are accompanied by COAs, MSDS, and SGS/BV certification (on request), ensuring compliance with international standards.

Fertilizers
MURIATE OF POTASH (MOP)
Chemical Name: Potassium Chloride
Chemical Formula: KCl
Common Name: MOP
HS Code: 31042000
Typical NPK Grade: 0-0-60
What is Muriate of Potash?
Muriate of Potash (MOP) is the most widely used potassium fertilizer in the world. It is composed primarily of potassium chloride (KCl) and contains a high concentration of potassium (K₂O) which is vital for plant development, water regulation, enzyme activation, and resistance to diseases.
It appears as white or red crystals or granules, depending on the origin and processing method.
Types of Muriate of Potash
| Type | Appearance | Key Application |
|---|---|---|
| Granular MOP | Larger red/pink granules | Direct application, blending |
| Standard MOP | Fine white crystals | Fertilizer manufacturing, foliar use |
| Industrial Grade MOP | Pure white crystals | Used in chemical, industrial sectors |
Uses of MOP
Agricultural Uses
- Provides potassium, essential for:
- Root development
- Photosynthesis
- Drought resistance
- Improved fruit size, color, taste
- Used for cereal crops, sugarcane, oilseeds, vegetables, and fruits
- Often used in bulk blending fertilizers (NPK mixtures)
Industrial Uses
- Used in the manufacture of:
- Potassium hydroxide (KOH)
- Potassium carbonate
- Detergents, soaps, dyes
- Water softeners
Typical Specifications – MOP (Agricultural Grade)
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Potassium as K₂O | Min. 60% |
| Potassium as KCl | Min. 95% |
| Moisture Content | Max. 0.5% |
| Sodium (NaCl) | Max. 2.0% |
| Insoluble Matter | Max. 1.0% |
| Appearance | Red/White crystalline granules |
| Solubility in Water | Completely soluble |
| pH (5% solution) | 6.5–7.5 |
Packing Options
- 25 kg & 50 kg woven bags with inner PE liner
- Customized bags with company logo and design
- 1 MT jumbo bags for bulk shipments
All exports come with:
- Certificate of Analysis (COA)
- MSDS and REACH documentation
- SGS/BV third-party inspection on request

Fertilizers
NPK FERTILIZER
Full Form: Nitrogen (N) – Phosphorus (P) – Potassium (K)
HS Code: 31052000 (for compound NPK)
What is NPK Fertilizer?
NPK fertilizer is a multi-nutrient blended or compound fertilizer that contains the three essential macronutrients required for plant growth:
- Nitrogen (N):Promotes leaf and vegetative growth
- Phosphorus (P):Encourages root development and flowering
- Potassium (K):Enhances overall plant health, disease resistance, and fruit development
NPK fertilizers can be customized into different ratios depending on crop requirements and soil conditions.
Types of NPK Fertilizer
1.Straight NPK Compound (Granular)
- Uniform granules containing all three nutrients
- Examples: NPK 15-15-15, 20-20-20, 12-32-16, etc.
2.Customized NPK Blends
- Tailor-made formulas for specific crops or regions
- Blended using single-nutrient fertilizers like Urea, DAP, MOP
3. Water-Soluble NPK (WSNPK)
- 100% soluble in water
- Used in fertigation, drip irrigation, and foliar spray
- Grades like 19-19-19, 13-40-13, 20-20-20, etc.
4. Coated or Controlled-Release NPK
- Slow-release granules with polymer/sulfur coatings
- Reduces nutrient loss and increases efficiency
Uses of NPK Fertilizer
- Suitable for vegetables, fruits, cereals, sugarcane, cotton, rice, oilseeds, etc.
- Used across all farming methods: open field, greenhouse, hydroponics
- Enhances:
- Plant growth
- Crop yield
- Root development & flowering
- Fruit quality & shelf life
- Can be applied:
- By broadcasting, top-dressing, or through irrigation systems
Typical Specifications – NPK 15-15-15 (Granular)
| Parameter | Typical Value |
|---|---|
| Total Nitrogen (N) | 15.0% |
| Phosphate (P₂O₅) | 15.0% |
| Potash (K₂O) | 15.0% |
| Moisture Content | ≤ 1.5% |
| Granule Size | 2–4 mm uniform |
| Appearance | Grey/blue/pink granules (varies by grade) |
| Solubility | Partial (for granular); Full (for WSNPK) |
Specifications vary by formula (e.g. NPK 12-32-16 has higher P content)
Packing Options
- 25 kg and 50 kg HDPE/PP bags with inner liner
- Customized printed bags with your brand name
- 500 kg and 1000 kg jumbo bags for bulk buyers
- Moisture-resistant, laminated packaging for humid environments
- Water-soluble NPK available in:
- 1 kg, 5 kg, 10 kg foil/laminated pouches
- 25 kg moisture-proof woven bags

Fertilizers
POTASSIUM NITRATE (KNO₃)
Chemical Formula: KNO₃
HS Code: 31059010
NPK Grade: 13-0-46
What is Potassium Nitrate?
Potassium Nitrate (KNO₃) is a highly efficient, water-soluble fertilizer containing 13% nitrogen (N) in nitrate form and 46% potassium (K₂O). It plays a key role in plant nutrition and is widely used in fertigation, hydroponics, and high-value crop cultivation. KNO₃ is also a key raw material in various industrial and technical applications.
It typically appears as a white crystalline powder or granules, non-hygroscopic and odorless.
Types of Potassium Nitrate
1.Agricultural Grade (Water-Soluble)
- Fine crystals or prills
- Used in fertigation, sprinklers, and foliar sprays
- Compatible with most fertilizers except those containing calcium
2.Technical/Industrial Grade
- Used in pyrotechnics, glass manufacturing and ceramics
- Higher purity, specific particle size and flowability
Uses of Potassium Nitrate
Agricultural Uses
- Promotes flowering, fruit development, and disease resistance
- Ideal for chloride-sensitive crops such as tobacco, potatoes, grapes, citrus, and tomatoes
- Widely used in:
- Greenhouse cultivation
- Hydroponics systems
- High-value fruit & vegetable farming
Typical Specifications – Agricultural Grade KNO₃
| Parameter | Typical Value |
|---|---|
| Nitrogen (as N) | Min. 13.0% (Nitrate form) |
| Potassium (as K₂O) | Min. 46.0% |
| Moisture | Max. 0.5% |
| Solubility in water | 100% |
| pH of 1% solution | 6.5 – 7.5 |
| Appearance | White crystalline powder or prills |
| Chloride Content | < 0.2% (Chloride-free) |
| Heavy Metals | < 10 ppm |
Packing Options
- 25 kg PP woven bags with inner polyethylene liner
- 50 kg standard bags(on request)
We offer third-party inspection certificates (SGS/BV), COAs, and MSDS with every shipment as per customer requirement.

Fertilizers
POTASSIUM SULPHATE (SOP)
Chemical Formula: K₂SO₄
HS Code: 31043000
NPK Grade: 0-0-50 (+17.5% S)
What is Potassium Sulphate (SOP)?
Potassium Sulphate (SOP) is a chloride-free potassium fertilizer containing 50% K₂O (potassium oxide) and 17.5% sulfur. SOP is especially important for chloride-sensitive crops, and provides both potassium and sulfur in plant-available forms. It is also known as Sulphate of Potash.
It is typically available as a white crystalline powder or granules, and is fully water-soluble depending on grade.
Types of SOP
1.Standard Grade SOP (Powder/Crystalline)
- Highly water-soluble
- Used in drip irrigation, foliar spray, and hydroponics
- Preferred in greenhouses and for precision agriculture
2.Granular SOP
- Larger granules (2–4 mm)
- Used for mechanical application and broadcasting
- Suitable for open-field agriculture
Uses of SOP
Agricultural Uses
- Supplies chloride-free potassium for high-value crops like:
- Grapes, citrus, melons, tobacco, potatoes, tea, and coffee
- Improves:
- Fruit size and sweetness
- Crop resistance to stress, drought, and pests
- Overall crop yield and quality
- Used in:
- Fertigation systems
- Broadcast application
- Blending with NPK formulations
Typical Specifications – SOP (Agricultural Grade)
| Parameter | Typical Value |
|---|---|
| Potassium (K₂O) | Min. 50.0% |
| Sulphur (as S) | Min. 17.5% |
| Moisture | Max. 1.0% |
| Chloride Content (Cl) | Max. 1.5% (low-Cl) |
| Water Solubility | 100% (for crystalline/powder SOP) |
| Appearance | White powder or granular |
| pH of 1% solution | 6.0 – 7.5 |
Industrial and technical grades may have different purity and pH ranges depending on the application.
Packing Options
- 25 kg and 50 kg woven bagswith inner PE liner
- 500 kg and 1000 kg jumbo bags for bulk customers
All products come with:
- SGS/BV certification (if required)
- Certificate of Analysis (COA)
- Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS)

Fertilizers
SPECIALTY FERTILIZERS
Category: High-efficiency, targeted nutrition solutions
Purpose: Improve nutrient uptake, reduce environmental losses, support precision agriculture
What Are Specialty Fertilizers?
Specialty fertilizers are advanced nutrient formulations that offer controlled release, site-specific delivery, or improved solubility and absorption. They are designed to maximize crop productivity, minimize nutrient loss, and enhance soil sustainability.
They differ from conventional fertilizers by offering enhanced efficiency, making them ideal for modern intensive farming systems.
Types of Specialty Fertilizers
1.Water-Soluble Fertilizers (WSF)
- Fully soluble in water
- Ideal for fertigation, drip irrigation, and foliar spray
- Examples: 19:19:19, 13:40:13, 20:20:20, etc.
2.Slow-Release Fertilizers (SRF)
- Nutrients are released slowly over time
- Reduced leaching and volatilization
- Examples: Urea-formaldehyde, sulfur-coated urea
3.Controlled-Release Fertilizers (CRF)
- Coated with polymer, sulfur, or resin
- Controlled nutrient release based on temperature and moisture
- Examples: Polymer-coated NPK, Osmocote™
4.Chelated Micronutrients
- Enhanced absorption of trace elements
- Stable across various pH levels
- Examples: Fe-EDTA, Zn-EDTA, Mn-DTPA
5.Liquid Fertilizers
- Easy to apply via fertigation or foliar spray
- Rapid absorption
- Available in single or multi-nutrient formulations
6.Bio-stimulants & Organic Fertilizers
- Improve nutrient uptake, root growth, stress tolerance
- Examples: Humic acid, seaweed extract, amino acids
Uses of Specialty Fertilizers
- Precision nutrient management in high-value crops: horticulture, orchards, floriculture, vegetables
- Improve yield quality, shelf life, and nutrient use efficiency
- Suitable for:
- Protected cultivation (greenhouses)
- Hydroponics
- Open-field precision farming
Typical Specifications
(Example: Water-Soluble NPK 19:19:19)
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Total Nitrogen (N) | 19% |
| Available Phosphorus (P₂O₅) | 19% |
| Soluble Potassium (K₂O) | 19% |
| Moisture Content | < 0.5% |
| Chloride (Cl) | Nil / <0.5% (low salt index) |
| Solubility | 100% in water |
| Form | Crystalline powder |
| Color | White or colored (as per formulation) |
Other specialty products will vary in nutrient ratio, chelating agent (e.g. EDTA, EDDHA), coating material (CRF), and pH levels.
Packing Options
- 1 kg / 5 kg / 10 kglaminated pouches (retail ready)
- 25 kg HDPE or BOPP bags(bulk use)
Cart (0 items)
Global Trade | Fertile Growth | Future Focused
►
Necessary cookies enable essential site features like secure log-ins and consent preference adjustments. They do not store personal data.
None
►
Functional cookies support features like content sharing on social media, collecting feedback, and enabling third-party tools.
None
►
Analytical cookies track visitor interactions, providing insights on metrics like visitor count, bounce rate, and traffic sources.
None
►
Advertisement cookies deliver personalized ads based on your previous visits and analyze the effectiveness of ad campaigns.
None
►
Unclassified cookies are cookies that we are in the process of classifying, together with the providers of individual cookies.
None






